Sytrus - Basics of FM TutorialINSTRUMENTS / GENERATORS Sytrus - Basics of FM Synthesis and the Modulation Matrix Basics of FM SynthesisMost of today's software synthesizers use a process known as 'subtractive synthesis' - a spectrum-rich oscillator (saw, square, triangle, etc.)is processed with a low-pass, band-pass, or high-pass resonant filter to produce the final sound. FM (Frequency Modulation) uses a differentapproach - pure tones (sine waves) processed in such a way that additional harmonics are created (one sine wave modulates the frequency of another)and added to the signal to produce the final sound. Unlike sub-synths, the basic module of the FM synth is called an 'operator', which includes apure tone oscillator (sine wave) and an articulation section. At the basic level the articulation section is at least a simple ADSR volume envelope.FM synthesizers contain two or more operators (Sytrus supports up to six operators). When an operator is connected to the input of another, apitch (frequency) modulation occurs (see diagram, above). The modulating operator is known as the 'modulator', while the modulated operator is calleda 'carrier' (in Sytrus a single operator can act both as a carrier and modulator).Sytrus ImplementationSytrus offers everything found in classic FM synthesizers and supports up to six operators and a modulation matrix, in which you can define thesynthesis algorithm.
Sytrus also includes a set of advanced features which allow you to create many unique sounds:. Custom Oscillator Shape - The oscillator shape of each operator can be tweaked in various ways, such as adding harmonics,morphing to shapes other than sine (square, triangle), pulse width, add noise, etc. An operator can also be set to generate plucked string toneswith a fully customizable damping envelope, which can be indispensable for string and pads patches. Ring Modulation - Besides FM (frequency modulation) and additive mixing, Sytrus operators can also interact in RM (Ring Modulation)mode.
Dec 23, 2015 We settle down this week for a comprehensive guide to using the multitalented Sytrus Synthesiser. Sytrus is a combination of Subtractive, FM and RM Synthesis and so understandably it can be quite.
Ring Modulation is the process by which two input signals are multiplied together to produce a new sound, often with characteristics which arequalitatively different from the original input signals. Support for Subtractive Synthesis - Sytrus includes three fully-featured SVF (filter) modules which can be used to filterthe operators' output. By combining both additive (FM/RM) and subtractive (SVF) synthesis techniques, Sytrus offers a very flexible means ofproducing a wide range of sounds, without the need for additional plugins or processing.
- Sytrus Tutorials. How to make 808s like Lex Luger In FL Studio FL Studio Tutorials, Sytrus Tutorials. How To Create Deep House Chord Stab With Sytrus FL Studio Tutorials, Sytrus Tutorials. MAKE BETTER MUSIC Subscribe to YOUTUBE Join 234,114+ music producers & get new tutorials daily!
- Use the Sytrus Generator in FL Studio - Part 14 of 16. Click through to watch this video on expertvillage.com. Use the Sytrus Generator in FL Studio - Part 15 of 16. Click through to watch this video on expertvillage.com. Use the Sytrus Generator in FL Studio - Part 16 of 16. Click through to watch this video on expertvillage.com.

Effects Module - Offers a range of effects to treat the patch sound, including three delay lines (which can process in parallelor serial mode) and a high-quality chorus effect to add depth to Sytrus patches. The signal from the effects module can also be sent to afor additional processing. Fully Customizable Articulation - Mapping diagrams, LFO and envelopes in Sytrus extend far beyond simple ADSR volumeenvelope support. Each diagram and envelope state can consist of of unlimited number of curve segments, with control of pitch, volume, panning,velocity mapping, and unison settings, etc. This allows for more complex patch structures, including even programming whole drum and synth loopsinto a single patch/voice. Programmable Unison Mode - Supports sub-level voices, variable pitch, pan, volume and envelope variation.
Uniquely, eachproperty targeted in the articulation sections of the modules can be mapped by the patch creator to the unison voices following 100% customizablemapping graphs, which allows almost every voice in the unison to have different properties (for more information, see themodule).NOTE: If you want to create your own Sytrus patches or modify existing ones, it is recommended to check the Sytrus processingdiagram. It describes in detail how the Sytrus modules are processed and mixed:The same diagram is quickly accessible from a button on the Sytrus interface:Modulation Matrix. The modulation matrix in Sytrus allowsyou to set up the FM synthesis algorithm and to adjust the operator send levels for effects and filter modules, and panning and 'dry'output levels.Each knob controls a specific function or mapping (as explained below). The neutral position for each knob is the middle Use Alt +Left-click to reset a knob to its neutral position.
You can also Right-click a knob to quickly mute/unmute, while preserving the knobvalue (this feature is useful when testing and tuning a patch)The modulation matrix comprises several discrete parts. Below we will take a more detailed look at each section and its applications: Modulation Setup. The FM/RM section sets up the modulation algorithm of Sytrus. Each row represents an operator and determines which operators will modulateit and by how much.The knobs determine the amount of modulation - if the value is negative (turn the wheel at left) the modulation phase willbe inverted. At the neutral level (Alt + Left-click a knob), there will be no modulation.It is not necessary for an operator to be modulated in order for it to produce output.Note - If you're unsure of the purpose of any knob in the matrix, simply hover over it with your mouse and check theFL Studio Hint Bar.Here are few very basic algorithms and their representation in the Sytrusmatrix:In these examples, Operator 1 is used as a carrier while the rest of the active operators are modulators.
You can modulate an operator by itself(in example 3 - row 2, column 2 - modulating operator 2 by itself), thus creating a feedback effect.Note that the carrier must be assigned an output, either directly (as in the examples), or via the filter modules. For more information on filtersand output assignment, see the other two matrix sections covered below.Sytrus also supports RM (ring modulation) interaction between operators. To see and adjust the RM setup, click the FM/RM switch at the bottom of thematrix:Please keep in mind the switch only affects the modulation setup section ofthe matrix, as the rest of the settings (pan, FX send, filter send, etc.) areshared among the FM/RM setups. Filter Send Levels.
This section adjusts the amountof signal sent from each operator to the filter modules. Negative values will send an inverted signal to the filter modules.Sytrus includes three filter modules. Each row in the section represents one module. If you want to send 50% of the output from operators 3 and 4to filter section 2, adjust the knobs as follows: in row F2 (filter section 2), adjust the knob in column 3 (operator 3) to 50%; in the same rowadjust the knob in column 4 (operator 4) to 50%.To reset a knob to a neutral position, use Alt + Left-click.Note that to hear the output of the filter sections, they need to be assigned an output.
How To Use Sytrus In Fl Studio 20
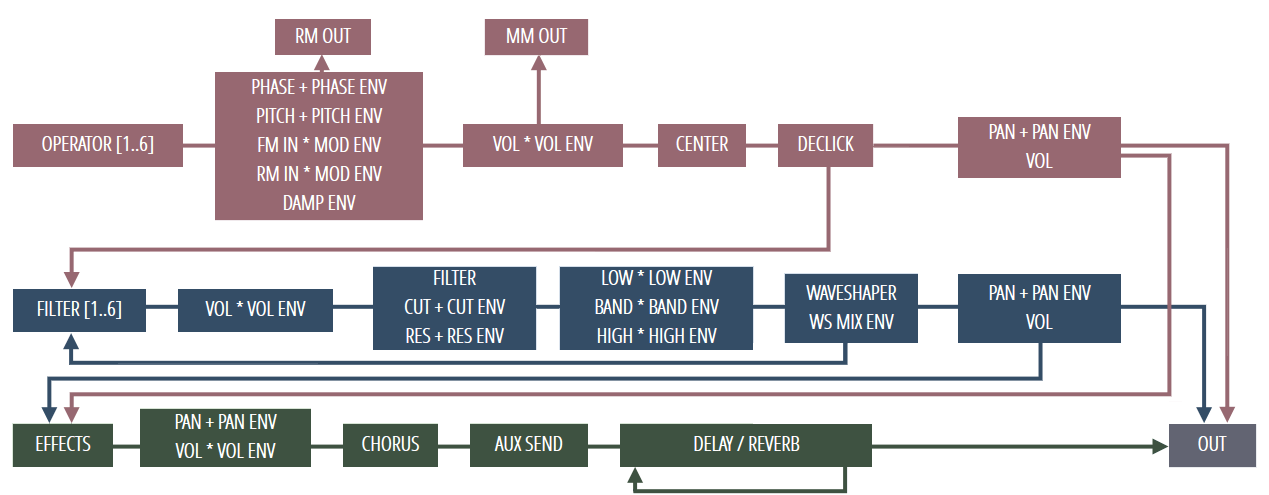
To learn more, see the Pan, FX Send andOutput section below. Pan, FX Send and Output. In this section you can definethe panning, effects send and output amounts for each of the operators and the three filter sections.The first column sets the panning of its corresponding module (operator or filter).
The default position is center.The second column defines the amount of signal sent to the effects module. If you set this knob to a negative value, an inverted signalwill be sent to the effects module. In the default neutral position (middle), no signal is sent to the effects module.The third column defines the output amount for its corresponding module (operator or filter). A negative value will send an inverted signalto the output.IMPORTANT: Neither the operators or filter modules in Sytrus produce audio automatically.
You'll need to use the matrixto rout them to the output stages as follows:1. Assign an output level for the module from the matrix section.2. Assign an effects send level for the module (the effects module is automatically sent to the output).3.
(operators only) Assign the operator a filter send level via the Filter Send Levels matrix section (see above). Thefilter module you send to needs to 'reach' an output by itself.4. (Filters only) Use the Send to Next knob (see the page for moreinfo).
Settle down this week for a comprehensive guide to using the multitalented Sytrus Synthesiser.Sytrus is a combination of Subtractive, FM and RM Synthesis and so understandably it can be quite difficult to understand where to start. In this course we break it all down.
How do you use the Ring Modulation / Matrix / Filters and more.We wrap it all up with some real world examples of using the synth to create some popular sounds. Use freenas for vmware vsan windows 7.